Pal histology muscular tissue lab practical question 15 delves into the fascinating world of muscular tissue, exploring its intricate structure, diverse types, and essential role in movement. This practical question serves as a gateway to understanding the fundamental principles of muscle histology, equipping students with the knowledge and skills necessary for accurate tissue analysis.
Muscular tissue, the primary tissue responsible for movement, exhibits remarkable diversity in its structure and function. From the striated fibers of skeletal muscle to the smooth contractions of visceral muscle, each type possesses unique characteristics that enable it to fulfill its specific roles.
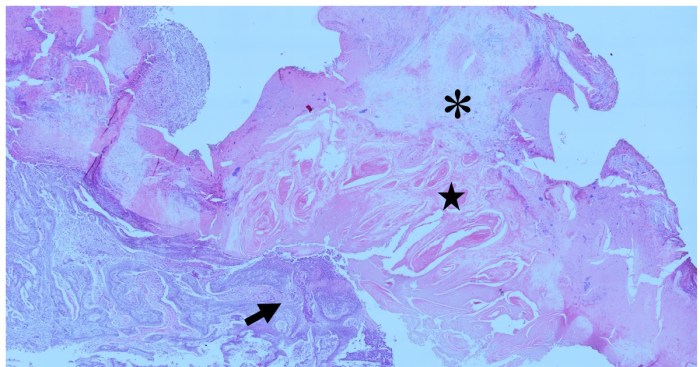
Histological techniques, such as staining and immunohistochemistry, provide valuable insights into the intricate architecture of muscular tissue, allowing researchers and clinicians to study its development, function, and pathology.
1. Muscular Tissue Histology Overview
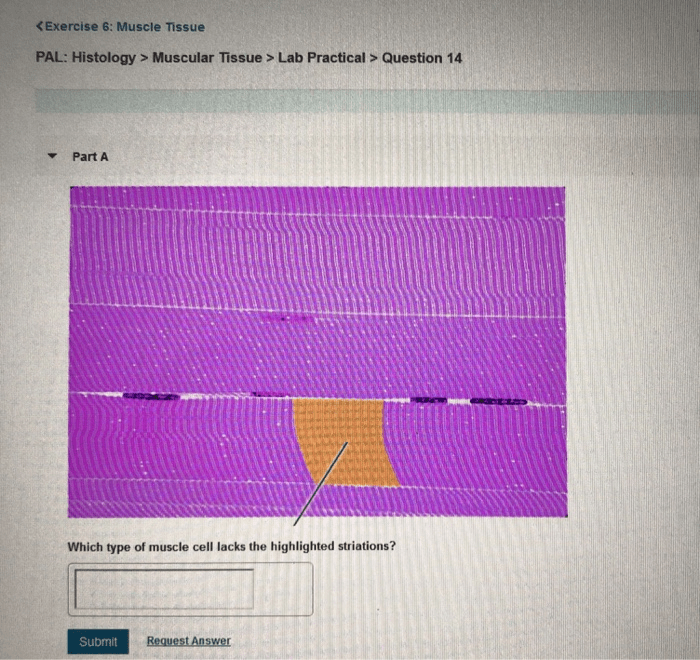
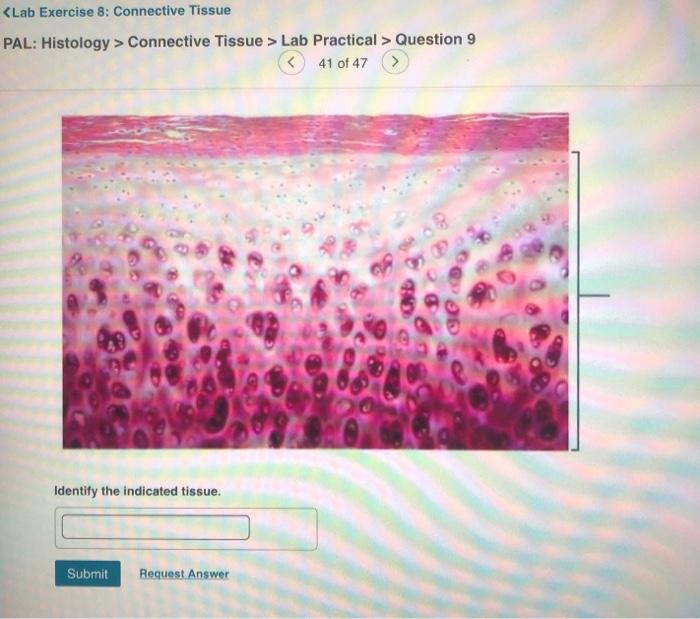
Muscular tissue is a type of connective tissue that is responsible for movement. It is composed of cells called muscle fibers, which are long, cylindrical cells that contain contractile proteins. These proteins allow muscle fibers to shorten, which in turn causes the muscle to contract.
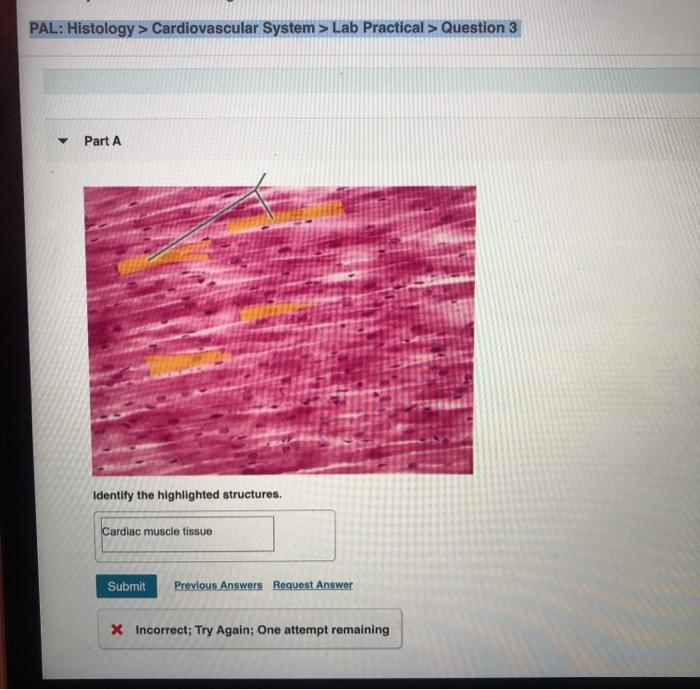
There are three types of muscular tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for voluntary movement. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of organs and blood vessels and is responsible for involuntary movement.
Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
2. Histological Staining Techniques for Muscular Tissue
Histological staining is a technique used to visualize different components of a tissue. There are a variety of histological staining techniques that can be used to visualize muscular tissue, including:
- Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining: This is a basic staining technique that uses hematoxylin to stain nuclei blue and eosin to stain cytoplasm pink.
- Trichrome staining: This staining technique uses three dyes to stain different components of the tissue. Masson’s trichrome staining is a common trichrome staining technique that uses hematoxylin to stain nuclei blue, Biebrich scarlet to stain cytoplasm red, and phosphomolybdic acid to stain collagen blue.
- Immunohistochemistry: This staining technique uses antibodies to visualize specific proteins in the tissue. Immunohistochemistry can be used to identify different types of muscle fibers, such as type I and type II muscle fibers.
3. Morphological Analysis of Muscular Tissue
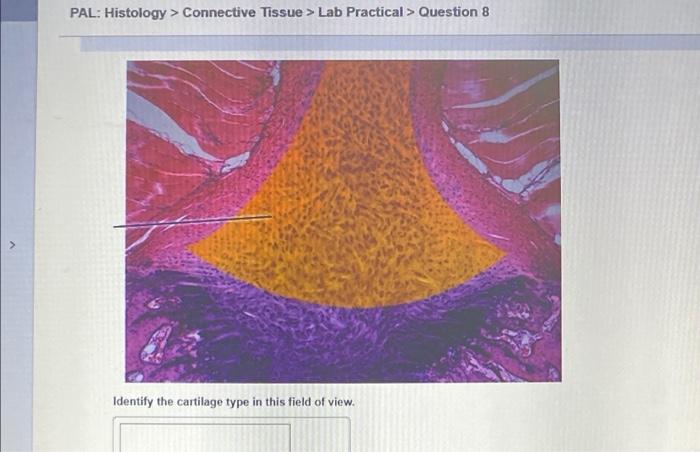
Morphological analysis is the study of the structure of a tissue. Morphological analysis of muscular tissue can be used to identify different types of muscle fibers and to assess the health of the muscle tissue.
Key morphological features of muscular tissue include:
- Fiber size: Muscle fibers can vary in size, from small to large. Fiber size is determined by the number of myofibrils in the fiber.
- Fiber shape: Muscle fibers can be round, polygonal, or fusiform. Fiber shape is determined by the arrangement of the myofibrils in the fiber.
- Fiber arrangement: Muscle fibers can be arranged in a variety of ways, including parallel, fascicular, and pennate arrangements. Fiber arrangement is determined by the function of the muscle.
4. Immunohistochemistry in Muscular Tissue Analysis, Pal histology muscular tissue lab practical question 15
Immunohistochemistry is a staining technique that uses antibodies to visualize specific proteins in the tissue. Immunohistochemistry can be used to identify different types of muscle fibers, such as type I and type II muscle fibers. It can also be used to study the expression of specific proteins in muscle tissue, such as myosin heavy chain and troponin.
Immunohistochemistry is a powerful tool for studying muscular tissue. It can be used to identify different types of muscle fibers, to study the expression of specific proteins, and to diagnose muscle diseases.
FAQ Corner: Pal Histology Muscular Tissue Lab Practical Question 15
What are the key morphological features of muscular tissue?
Key morphological features include fiber size, shape, arrangement, and the presence of striations or smooth appearance.
How does immunohistochemistry aid in muscular tissue analysis?
Immunohistochemistry allows researchers to visualize and localize specific proteins within muscle fibers, providing insights into their expression and distribution.
What is the significance of histological evaluation in muscular tissue disorders?
Histological evaluation helps identify and characterize muscle disorders, aiding in diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring treatment response.