Enter the iupac name of the ester depicted below – Embark on a journey to decipher the intricacies of ester nomenclature with the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge to confidently assign IUPAC names to esters, ensuring clear and precise communication within the scientific community.
Introduction
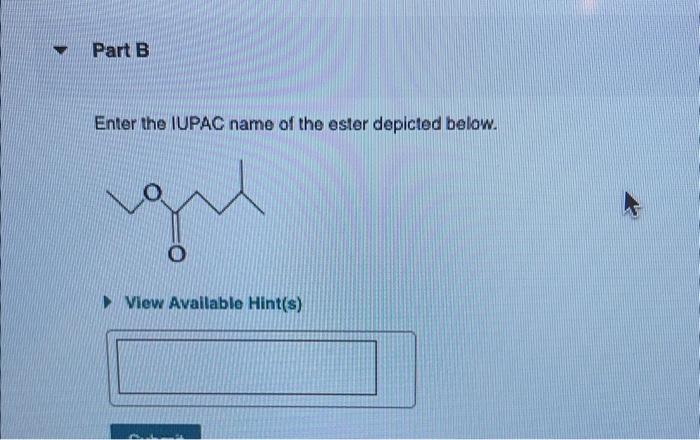
An ester is an organic compound derived from the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol. Esters are characterized by their general structure, which consists of an alkyl or aryl group bonded to a carbonyl group (C=O), which is in turn bonded to an alkoxy group (O-R).
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has established a system of nomenclature for esters that provides a systematic way to name these compounds.
Identifying the Functional Groups
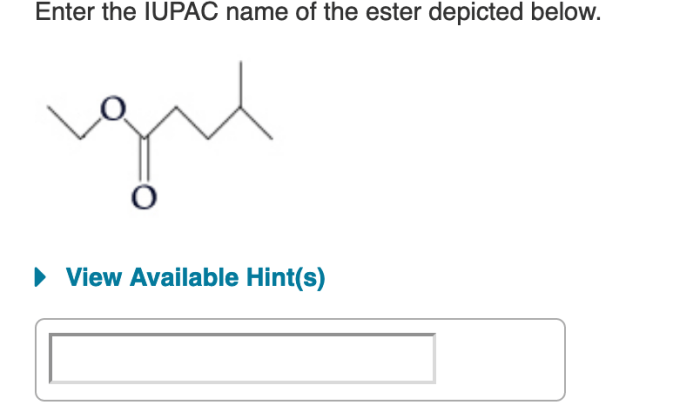
To name an ester using IUPAC nomenclature, the first step is to identify the carboxylic acid and alcohol components of the ester. The carboxylic acid component is the part of the ester that contains the carbonyl group, while the alcohol component is the part of the ester that contains the alkoxy group.
Once the carboxylic acid and alcohol components have been identified, the parent chain for each component can be determined.
Numbering the Carbon Chains
The next step is to number the carbon chains of the carboxylic acid and alcohol components. The carbon chain of the carboxylic acid component is numbered starting from the carbonyl carbon, while the carbon chain of the alcohol component is numbered starting from the carbon atom that is bonded to the oxygen atom of the alkoxy group.
The principal functional group, which is the carbonyl group in the case of esters, is assigned the lowest possible number.
Naming the Alkyl and Acyl Groups, Enter the iupac name of the ester depicted below
The alkyl group derived from the alcohol component is named using the IUPAC rules for naming alkanes. The acyl group derived from the carboxylic acid component is named by replacing the -ic acid suffix of the carboxylic acid with the -yl suffix.
For example, the acyl group derived from ethanoic acid is called the ethyl group.
Combining the Names
The IUPAC name of the ester is formed by combining the names of the alkyl and acyl groups. The name of the alkyl group is placed first, followed by the name of the acyl group. For example, the IUPAC name of the ester formed from the reaction of ethanoic acid with methanol is ethyl ethanoate.
Special Cases
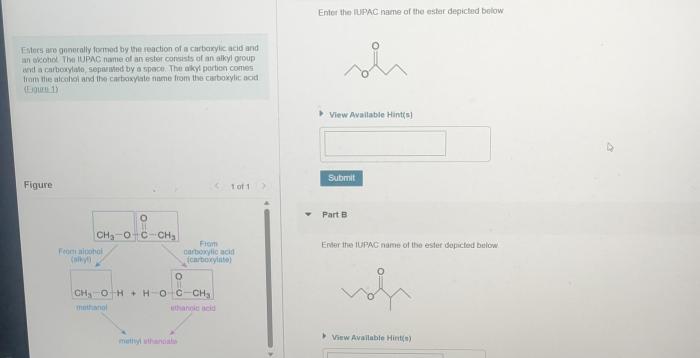
There are some special cases that can arise when naming esters using IUPAC nomenclature. For example, if the ester is formed from a cyclic carboxylic acid, the name of the ester will include the prefix cyclo-. Additionally, if the ester is formed from an unsaturated carboxylic acid, the name of the ester will include the suffix -enoate.
Additional Information
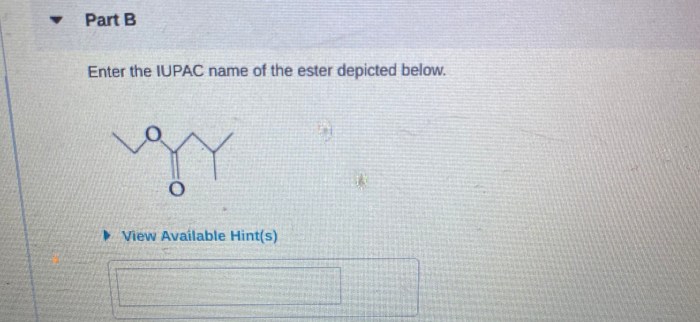
IUPAC nomenclature is a powerful tool that can be used to identify and classify esters in chemical reactions. It is also important for scientific communication, as it provides a standardized way to name these compounds. By understanding the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, chemists can effectively communicate about esters and other organic compounds.
Questions Often Asked: Enter The Iupac Name Of The Ester Depicted Below
What is the significance of IUPAC nomenclature for esters?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a systematic and globally recognized method for naming esters, ensuring uniformity and clarity in scientific communication and research.
How do I determine the parent chain for each component of an ester?
The parent chain for the alcohol component is the longest carbon chain containing the oxygen atom of the hydroxyl group, while the parent chain for the carboxylic acid component is the longest carbon chain containing the carboxyl group.
What are some special cases or exceptions to the general IUPAC naming rules for esters?
Cyclic esters, esters with branched alkyl groups, and esters with functional groups other than alkyl or acyl groups may require modifications to the general IUPAC naming rules.